It’s important to know about data types and one that comes up fairly regularly is that of Linked Lists.
Let’s write the following base code to create a Linked List.
# Defintion of a single Node
class Node:
# takes input data and next node
def __init__(self, data = None, next=None):
self.data = data
self.next = next
# Definition of a Linked List
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Insert a node into our Linked List
def insert(self, data):
newNode = Node(data)
if(self.head):
current = self.head
while(current.next):
current = current.next
current.next = newNode
else:
self.head = newNode
# Print our Linked List so we can see how it looks
def render(self):
current = self.head
while(current):
print(current.data)
current = current.next
Now that we have a base class, let’s insert a couple of nodes and print it out to see what we are working with:
# Define our LinkedList
ll = LinkedList()
# Insert a couple of nodes
ll.insert(1)
ll.insert(2)
ll.insert(3)
ll.insert(4)
# Render it out to the screen
ll.render()
What do we need to do to reverse this linked list?
Let’s start by creating a reverse function.
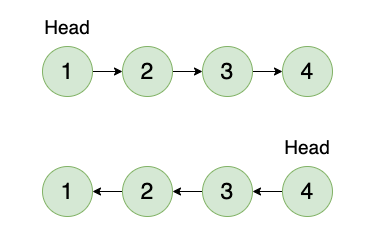
We should know that:
- All the links start pointing in the opposite direction
- The head starts to point to the last element of the list
Using an iterative approach, let’s start writing our function.
We will need to create a couple of variables to keep track of the position of each of our nodes as we loop through.
Some things to note:
previous initially points to None. This becomes the head on consecutive calls.
current points to the first element. This is the current head element point.
following points to the second element. This is the next element point.
# takes a `list` input
def reverse(list):
# initialize our 3 main variables
previous = None
current = list.head
following = current.next
# keep looping until at the end of the list
while current:
# reverse the link
current.next = previous
previous = current
current = following
# if there are more nodes and this isn't the end
if following:
following = following.next
# set the head to the previous item
list.head = previous
Let’s test it!
# Define a LinkedList
ll = LinkedList()
# Insert some nodes
ll.insert(1)
ll.insert(2)
ll.insert(3)
ll.insert(4)
# Render our list in it's current order
print("Linked List")
ll.render()
# Reverse the list
reverse(ll)
# Render our list in it's new order
print("Reversed Linked List")
ll.render()
You know know how to reverse a list in Python!
